Tyre Types
Tyre Types On The Basis of Construction
There are two distinct types of construction for tyres - Bias ply and Radial ply. The construction method affects the durability, ride and fuel economy of the tyres. In India Radial tyres are the most common on cars and trucks are still largely on Bias Tyres.
Bias Type Construction - Tyres have belts called plies that give a tyre its shape. Plies may be the layers of Polyester, Fiberglass or Steel Cords embedded in the rubber of a tyre. A Bias-ply tyre has the layered belts running at angles to each other and to the body of the tyre.
Radial Type Construction
Radial-ply tyres have the belts at a 90-degree angle to the tyre, and the belts overlap rather than cross each other. Radial tyres have another belt, usually of steel cord, running around the tyre under the tread. Radial construction allows the sidewall of the tyre to flex under loads without affecting the contact of the tread with the road.
Advantages of Radial Tyres
Michelin introduced and patented the radial tyre in 1946. Since then, radial type construction has been recognized in the world for its advantages over the bias tyres. There are still applications where bias tyres are suitable, but radials offer benefits that bias tyres cannot. These benefits make radials a preferred choice for the most.
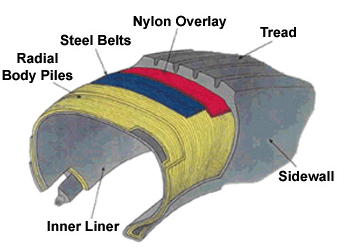
Construction
The advantages of a radial tyre are due, in part; to the way the tyre is constructed. Coated steel cables run from bead to bead perpendicular to the circumferential center line of the tyre. Steel belts are then laid over the radial plies under the tread of the tyre. This forms a two-part construction in which the sidewalls are a separate unit from the tread structure.
Puncture Resistance
The strength of the multi-layers of steel belts makes the tread resistant to punctures. The two-part type construction of the tyre structure allows the sidewalls to flex independently from the tread. This allows the tread to stay in contact with the road surface even while the sidewalls flex under a load or while cornering. This greatly reduces the chance of foreign objects puncturing the sidewalls since the sidewall doesn't "roll over" to present itself to the road surface.
Traction
The same construction elements that make the radial tyre puncture resistant also give it better traction than bias ply tyres. The radial's tread stays in contact with the road surface even under a load. A bias ply tyre will distort its tread under a load and so it reduces the amount of tread area that is in contact with the road surface.
Heat Efficiency
The steel cables in radial tyres act as a heat sink to neutral the affect of heat. This keeps the tyre running at a cooler temperature than an equivalent - sized bias tyre. The plies of a bias tyre hold heat and so are more prone to blowouts when the tyre heats up during sustained highway driving.
Quiet Ride
The radial tyre-due to its two-part construction-offers a quieter, smoother ride than the bias tyre. It is also more fuel efficient since it offers less resistance to the road surface. This is a term referred to as "rolling resistance." Overall, radial tyres have longer life compared with bias tyres under similar workloads and environments.


