Air Classifying Mill
Air Classifying Mill is used for separating dry materials into different particle size fractions by their size, mass or shape also modify a particle size distribution. We have established a note worthy status among the Air Classifying Mill Manufacturers in India. We bring for the clients Air Classifying Mill of exceptional quality at cost-effective price.
- Resistance to wear and tear
- Sturdy build
- Easy installation
- Compactness
- Simple design
- Low maintenance
- Cost-efficiency
- Superior quality
Used In The Production Of :
- Aluminium Oxide
- Calcined Magnetite
- Cement
- Talc
- Metallurgical Powders
- Fly Ash
- Soya flour
- Food Products
- Graphite
- P.V.C. Resin
- Limestone
- Clays
- Pigments
- Silica
- Hydrated lime
- Chemicals
Operating Principle
Referring to the schematics below, most of the processing air or gas enters through the bottom section of the mill. Up to 30% of the total airflow can be introduced with the feed material. Concurrent with this constant mass flow of gas, feed material is introduced to the mill ideally in a constant mass flow manner.
For most applications, material is introduced to the tip of the rotating hammers through a port opening at the side of the mill. Feed material can be either pneumatically conveyed or screw fed. The rotating hammers attached to the impact rotor disc serve to fracture the process material.
A serrated liner mounted on the periphery of the grinding chamber in the hammer path serves to improve grinding efficiency by preventing particles from accelerating to the speed of the hammers thereby increasing the relative speed difference.
The primary airflow passing through the narrow annular gap formed in between the liner and impact rotor disc in conjunction with the fanning action of the hammers transports the material to the top of the mill. A dispersion ring then directs the material downward toward the classifier. Baffles welded to a shroud ring straighten the flow of material and air so that particle vortexing at the dispersion ring area is avoided.
The shroud assembly effectively separates the grinding zone from the classification zone as well as providing a defined path for the material and air to flow through.
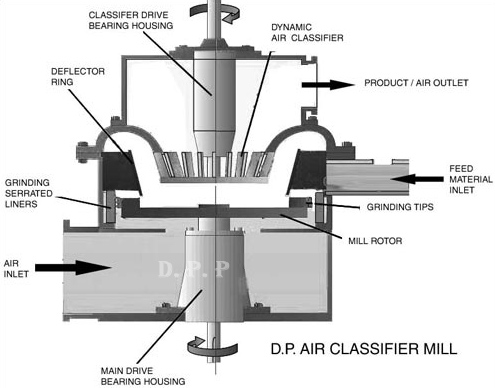
Depending upon the air flow rate and separator speed adjustment, discreet particles are acted upon by either the center seeking drag force of the air that flows through the classifier or the center fleeing centrifugal forces created by the turning of the classifier wheel. Rejected particles fall by gravity and are pulled back under the shroud assembly to the spinning hammers for further impact.
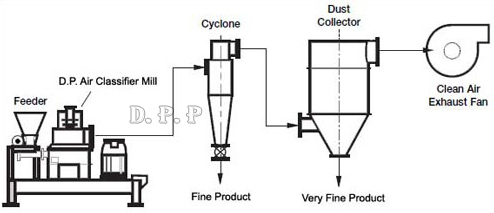
Specifications
Air Classifier Mill Size |
D.P.A.C.M. -100 |
D.P.A.C.M. -300 |
D.P.A.C.M. -600 |
| Main Drive motor (HP) | 10 | 30 | 60 |
| Classifier Motor (HP) | 1 | 5 | 10 |
| Rotor Speed (Max RPM) | 7000 | 4700 | 2900 |
| Classifier Speed (Max RPM) | 4500 | 2500 | 2000 |
| Max Air Flow (Max m3/hour) | 1300 | 3500 | 6500 |
Air Classifier Mill - 01 Air Classifier Mill - 02
.jpg)

