Calorised & Ceramic Coated Pipes
KANDI introduced CALORISED & CERAMIC COATED PIPES (CCCP) for Indian and Global Steel Making Shops to increase the lance life beyond conventional black steel pipes and coated pipes.
Calorised lance pipe is made up of 5 layers. At the core is a high quality mild steel lance pipe. By calorisation, a thickness of 100-150 microns is imparted on outer surface, and further coating with refractory materials in 200-300 microns thickness on both inner and outer surfaces, the diffusion is an inter metallic bond, which doesn’t get damaged either by mechanical working like bending or straightening or by high temperatures. In the case of metal diffused pipes, the metal existing at the surface of the diffused zone is oxidized to the respective oxide, which prevents the further progress of oxidation and also melting. For instance, by calorisation, aluminium is oxidized alumina, which has a very high melting point of 2050 oC compared to the melting point of aluminium, which is mere 658 oC.
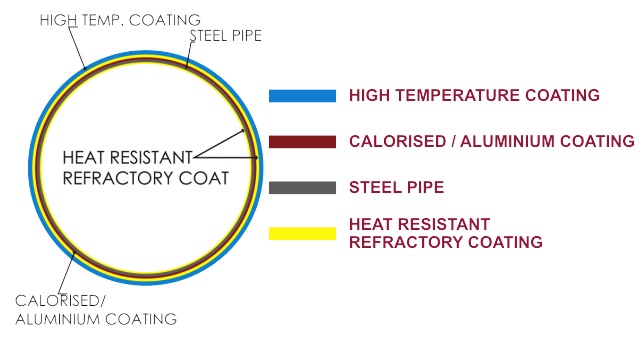
In the process of steel manufacturing by open hearth or electric furnace, the consumption rate of lance pipes for oxygen injection slows rather high ratio owing to high temperature severe oxidation. In general, steel pipes are used as lance pipes for oxygen injection. If MS pipes are treated by Calorisation process, consumption rate of lance pipes will decrease 5-8 times. Research conducted over many years revealed that the most effectual method is to diffuse aluminum into the pipe’s surface, so as to promote where proof properties on steel pipe. Calorising is carried outside of the steel pipe to promote wear and fire proof properties of the pipe.
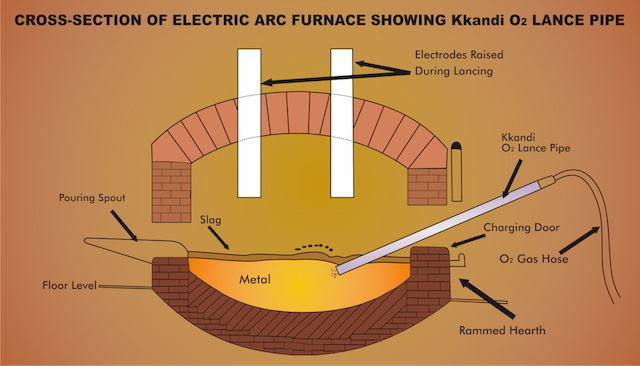
MS pipes are calorised on outer surface, and are thereafter given Ceramic Coating on both inner and outer surface after the calorizing treatment. Ceramic coating gives an extra ordinary higher life and resistance to corrosion at high temperature than ordinary MS pipes and expensive stainless and alloy steel pipes normally used in oxygen lancing in electric arc furnaces and chemical factories and refineries. The average life of calorised with ceramic coated pipes is 5-8 times more than that of ordinary MS Pipes and Stainless Steel Pipes.
| TYPE 1 | Both ends threaded with one coupling and one plastic cap | |
| TYPE 2 | Both ends threaded with one coupling and one plastic cap | |
| TYPE 3 | No Threads | |
| TYPE 4 | No threads with one press coupling |
| N.B & SERIES | OD | WALL THICKNESS | STD LENGTH* | COATING THICKNESS COVERED |
| mm | mm | mm | mm | MICRONS |
| 08 | 13.4 | 1.7 – 1.8 | 5500 | 250 avg. |
| 10 | 16.9 | 1.8 – 1.9 | 5500 | 250 avg. |
| 15 | 21.2 | 2.0 – 2.1 | 5500 | 300 avg. |
| 20 | 26.9 | 2.3 – 2.4 | 5500 | 350 avg. |
| 25 | 33.8 | 2.5 – 2.6 | 5500 | 400 avg. |
| 32 | 42.5 | 2.5 – 2.7 | 5500 | 400-450 avg. |
| 40 | 48.4 | 2.8 – 3.0 | 5500 | 400-450 avg. |
To enumerate the advantages of these pipes in oxygen steel making process are:
- The exothermic reaction and agitation promote decarbonisation and heat rise in the furnace, while foaming slag can be eliminated.
- Fusion of sub material can be accelerated.
- Quality of steel will be improved.
- As the process raises the temperature.
- Selection of raw materials to be charged becomes easy.
- The process raises the production capacity of an electric furnace.
- Hydrogen,Nitrogen and non-metallic inclusions can be eliminated through oxidation.
- It makes it possible to recover chrome with the use of high chrome steel scrap.
To summarize, Calorised & Ceramic Coated Pipe (CCCP) is carbon steel pipe with calorisation on outer surface of pipe, and thereafter multiple, thin layers of ceramic coating both exteriorly and interiorly. The outer surface of ceramic coating on pipe is resistant to slag attack and extends the life of the pipe when it is immersed into molten metal or in high temperature atmospheres. The CCCP applications include powder injections, tap-hole cleaning and opening nozzles is ladles, tundish and launders.
- Cutting scrap, raising bath temperatures and decarburizing
- Opening nozzles in tundish and ladles
- Injecting carbon and other powders into the electric furnace and ladle
- Opening the iron notch of a blast furnace
- Injecting argon into ladles
- Injecting argon and oxygen into the A.O.D. furnace
- Injecting flux for degassing in aluminum melting furnaces
| Oxygen Charge Pressure (Kg/cm2) | Oxygen flow rate (m3/min) | Charge Time (min.) | Length of consumption (mm) | Consumption rate (mm/min) | Type of Pipe | Rate of MS Pipe to Calorised Lance |
| 6.5-7 | 6.5-5 | 3 | 1950 | 650 | MS | 1 |
| 6.5-7 | 6.5-5 | 15 | 1420 | 94 | CCCP | 6.91 |
| 6 | 6 | 3 | 2430 | 809 | MS | 1 |
| 6 | 6 | 10 | 1150 | 115 | CCCP | 7.03 |
| 5.5-6 | 5.5 | 3 | 1860 | 620 | MS | 1 |
| 5.5-6 | 5.5 | 10 | 840 | 84 | CCCP | 7.38 |
