Heat Exchangers
Simply put, a heat exchanger is a heat transfer device that exchanges heat between two or more process fluids. Heat exchangers have wide industrial application and can be classified based on their functions such as Condensation, Boiling, Heating, Cooling and Evaporation.
A shell and tube heat exchangers (STHEs) are the most common type of heat exchangers and are predominantly used in high pressure and high temperature conditions.
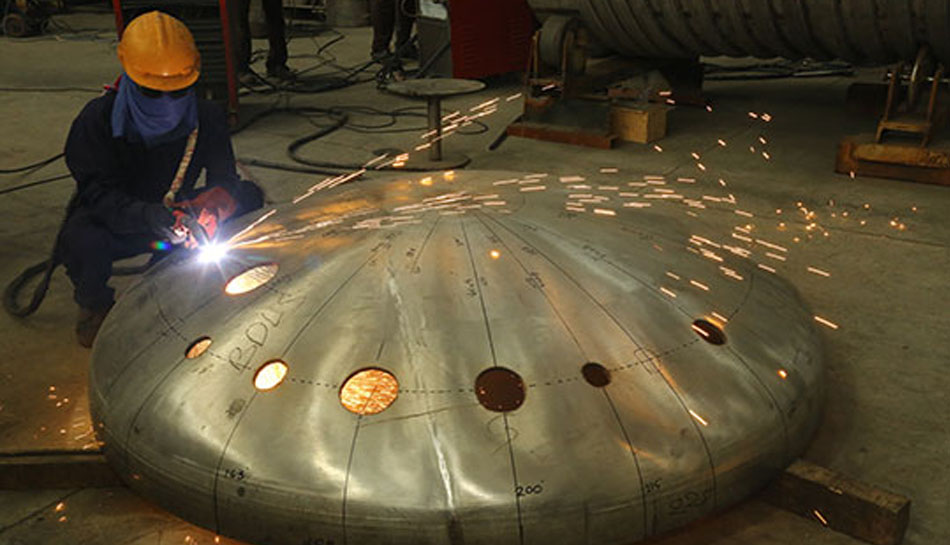

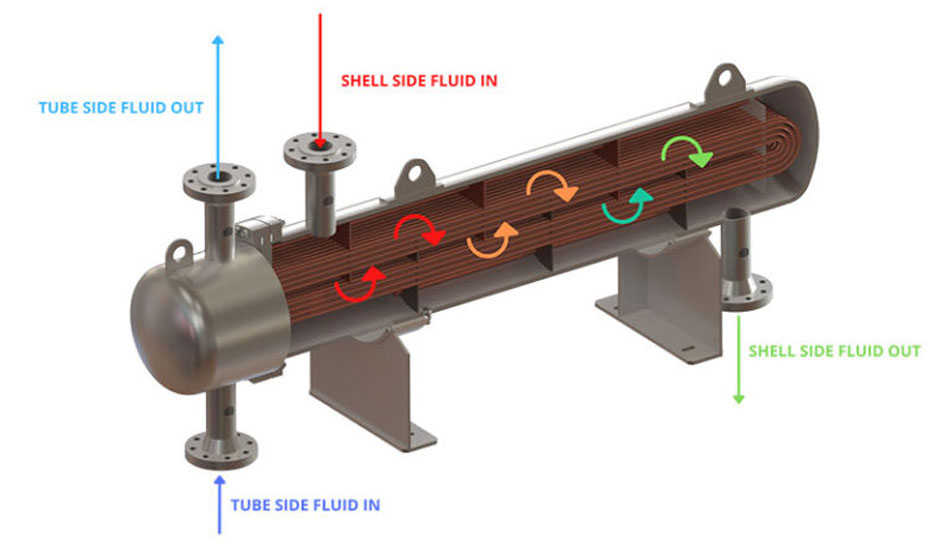
A Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger
A Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger consists of a series of tubes (tube bundle), arranged or stacked within a cylindrical shell. As depicted in the diagram above, each tube passes through a series of baffles and tube sheets. One of the fluids flows on the outer side of the tubes and is referred to as shell-side stream, while the other flows within the tubes and is referred to as tube-side stream. The fluids can be single or two phase, and the tubes and shells can be configured as co-current (both streams flowing in the same direction) or as counter current (both streams flowing in the opposite direction). This causes heat exchange between the shell-side and the tube-side streams.
HEAT EXCHANGERS
As the shell-side stream passes in a sinusoidal way along the gaps created by the baffles, it experiences turbulence, which keeps the outsides of the tubes, and inside of the shell free from any deposits.
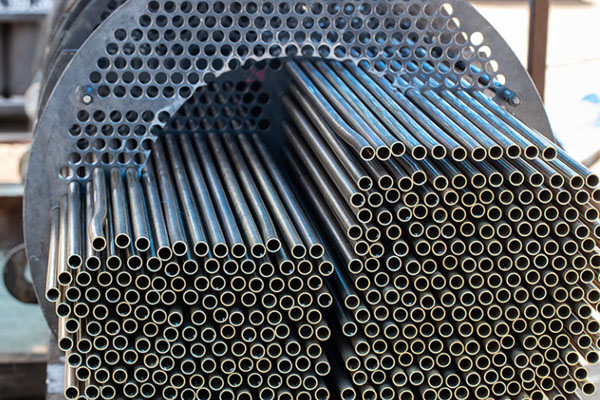
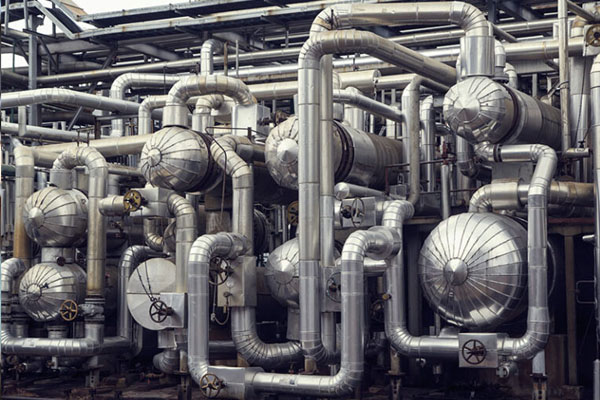


Shell and Tube types Heat Exchangers can also be classified into fixed type and floating type heat exchangers. The fixed type heat exchangers, the tube sheets are completely welded to the shell and acted as shell flanges. They are used for processes where inter-mixing of the two streams needs to be completely avoided.
In the floating type heat exchangers the tube bundle can be removed to clean the outer side as well as the inner sides of tubes and shell.
Apart from the fixed type and the floating type heat exchangers there is a 'U' shaped STHEs. Here the tubes are bundled in a 'U' shape by mechanical rolling to only one tube sheet. They are built with removable shell and tube to allow easy access for maintenance purposes.
ACME'S Shell and Tube heat exchangers are designed and fabricated as per codes and standards (ASME & TEMA) to meet the target quality for the process and industry standards. We use advanced technology in our design process and include both thermal and mechanical aspects to ensure optimum performance and efficiency.

Our workflow across departments is well aligned for smooth transition, right from study, design, prototyping, production, quality control and commissioning.
The expertise gained by our engineers in the design and fabrication of STHEs have helped ACME establish leadership in heat exchanger manufacturing for various process requirements. ACME heat exchangers have been deployed as Condensers, Reboilers, Heaters, Coolers, Falling Film Reboilers, Kettle Reboilers, Thermo Syphon Reboilers across industries. ACME has been recognised to have supplied highest heat exchanger area of 233 m2 and highest pressure of 33 bar – SS316.